-
 Cutting to the core of how 3D structure shapes gene activityIn biology textbooks and beyond, the human genome and DNA therein typically are taught in only one dimension. While it can be helpful for learners to begin with the linear presentation of how stretches of DNA form genes, this oversimplification undersells the significance of the genome's 3D structure.... Read more
Cutting to the core of how 3D structure shapes gene activityIn biology textbooks and beyond, the human genome and DNA therein typically are taught in only one dimension. While it can be helpful for learners to begin with the linear presentation of how stretches of DNA form genes, this oversimplification undersells the significance of the genome's 3D structure.... Read more -
 Antibody mapping chip speeds up vaccine research by revealing hidden binding sites quicklyA new microchip invented by Scripps Research scientists can reveal how a person's antibodies interact with viruses—using just a drop of blood. The technology offers researchers faster, clearer insights that could help accelerate vaccine development and antibody discovery.... Read more
Antibody mapping chip speeds up vaccine research by revealing hidden binding sites quicklyA new microchip invented by Scripps Research scientists can reveal how a person's antibodies interact with viruses—using just a drop of blood. The technology offers researchers faster, clearer insights that could help accelerate vaccine development and antibody discovery.... Read more -
 Time machine in drones? Photorealistic depiction shows Great Hungarian Plain before water regulationsMany of us have wondered what a landscape we see in a modern photograph might have looked like centuries ago. This question is especially intriguing when we know that the scenery has been radically transformed by human intervention over the past centuries.... Read more
Time machine in drones? Photorealistic depiction shows Great Hungarian Plain before water regulationsMany of us have wondered what a landscape we see in a modern photograph might have looked like centuries ago. This question is especially intriguing when we know that the scenery has been radically transformed by human intervention over the past centuries.... Read more -
 New AI tool models protein dynamics, aiding drug discovery and protein researchA major scientific advance in protein modeling developed by Microsoft Research AI for Science, has been published in Science. The study introduces BioEmu, a generative deep learning system that emulates the equilibrium behavior of proteins with unprecedented speed and accuracy.... Read more
New AI tool models protein dynamics, aiding drug discovery and protein researchA major scientific advance in protein modeling developed by Microsoft Research AI for Science, has been published in Science. The study introduces BioEmu, a generative deep learning system that emulates the equilibrium behavior of proteins with unprecedented speed and accuracy.... Read more -
 Scientists develop novel recording tool to monitor protein kinase activities in living cellsThe ability of protein kinases to transfer a phosphate group to target proteins plays an important role in many cellular processes. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg have now developed a novel molecular tool that can monitor these kinase activities both spatially and temporally. This... Read more
Scientists develop novel recording tool to monitor protein kinase activities in living cellsThe ability of protein kinases to transfer a phosphate group to target proteins plays an important role in many cellular processes. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg have now developed a novel molecular tool that can monitor these kinase activities both spatially and temporally. This... Read more -
 Algae unlock a cheaper, greener and more ethical way to grow cellsThe time it takes to grow new skin for burns victims could be improved thanks to a new method of cell cultivation using algae, developed by University of Queensland researchers.... Read more
Algae unlock a cheaper, greener and more ethical way to grow cellsThe time it takes to grow new skin for burns victims could be improved thanks to a new method of cell cultivation using algae, developed by University of Queensland researchers.... Read more -
 Drone herbicide applications prove effective for common reed controlNew research from the University of Waterloo shows that a single, targeted herbicide application from a Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) can suppress common reed invasions with more than 99% effectiveness. This result is among many research findings recently published online in Invasive Plant Science and Management.... Read more
Drone herbicide applications prove effective for common reed controlNew research from the University of Waterloo shows that a single, targeted herbicide application from a Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) can suppress common reed invasions with more than 99% effectiveness. This result is among many research findings recently published online in Invasive Plant Science and Management.... Read more -
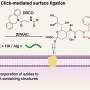 Sugar-coated 'sticky' stem cells could unlock surgery-free liver treatmentsA new process could help to treat liver disease without needing an organ transplant, a new study reveals.... Read more
Sugar-coated 'sticky' stem cells could unlock surgery-free liver treatmentsA new process could help to treat liver disease without needing an organ transplant, a new study reveals.... Read more -
 Newly discovered enzyme could play crucial role in bacterial breakdown of plasticsLeiden researchers have discovered an enzyme that helps bacteria feed on everyday plastics. This common enzyme could play a crucial role in future research and eventually in addressing the global plastic crisis. The study is published in Nature Communications.... Read more
Newly discovered enzyme could play crucial role in bacterial breakdown of plasticsLeiden researchers have discovered an enzyme that helps bacteria feed on everyday plastics. This common enzyme could play a crucial role in future research and eventually in addressing the global plastic crisis. The study is published in Nature Communications.... Read more -
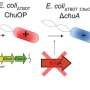 Scientists use AI to create protein that kills E. coliIn the last year, there has been a surge in proteins developed by AI that will eventually be used in the treatment of everything from snakebites to cancer. What would normally take decades for a scientist to create—a custom-made protein for a particular disease—can now be done in seconds.... Read more
Scientists use AI to create protein that kills E. coliIn the last year, there has been a surge in proteins developed by AI that will eventually be used in the treatment of everything from snakebites to cancer. What would normally take decades for a scientist to create—a custom-made protein for a particular disease—can now be done in seconds.... Read more -
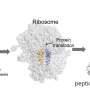 First-ever ribosomal synthesis of cyclic peptides opens new avenues for next-generation drug designInside our cells, ribosomes—the tireless "protein factories" of life—have just shown off a new skill they haven't used in billions of years. A research team has become the first in the world to successfully expand the range of ring-shaped backbones in proteins using ribosomes, which have traditionally only produced linear... Read more
First-ever ribosomal synthesis of cyclic peptides opens new avenues for next-generation drug designInside our cells, ribosomes—the tireless "protein factories" of life—have just shown off a new skill they haven't used in billions of years. A research team has become the first in the world to successfully expand the range of ring-shaped backbones in proteins using ribosomes, which have traditionally only produced linear... Read more -
 New software promises to make precision genome editing with CRISPR accessible to more researchersA Ph.D. student in biomolecular engineering at the University of California, Santa Cruz, has built a software program designed to facilitate the kind of precision genome editing involved in the development of cutting-edge therapeutics for genetic conditions such as certain metabolic or blood disorders, like sickle-cell anemia.... Read more
New software promises to make precision genome editing with CRISPR accessible to more researchersA Ph.D. student in biomolecular engineering at the University of California, Santa Cruz, has built a software program designed to facilitate the kind of precision genome editing involved in the development of cutting-edge therapeutics for genetic conditions such as certain metabolic or blood disorders, like sickle-cell anemia.... Read more -
 Fungicides intended to suppress turfgrass diseases may damage fairwaysGolf course managers have much more insight into which fungicides to use to suppress turfgrass diseases, such as the common and costly dollar spot disease, without damaging the grass on their fairways, thanks to a new study by researchers at Penn State.... Read more
Fungicides intended to suppress turfgrass diseases may damage fairwaysGolf course managers have much more insight into which fungicides to use to suppress turfgrass diseases, such as the common and costly dollar spot disease, without damaging the grass on their fairways, thanks to a new study by researchers at Penn State.... Read more -
 The multitasking microbe that turns CO₂ into mineralsAt more than 470 times the atmospheric concentration of CO₂, a humble soil bacterium does something extraordinary: it turns gas into stone.... Read more
The multitasking microbe that turns CO₂ into mineralsAt more than 470 times the atmospheric concentration of CO₂, a humble soil bacterium does something extraordinary: it turns gas into stone.... Read more -
 AI-powered strategy streamlines protein engineering by integrating structural and evolutionary constraintsA team of researchers has developed a method that could transform the field of protein engineering. The new approach, called AI-informed Constraints for protein Engineering (AiCE), enables rapid and efficient protein evolution by integrating structural and evolutionary constraints into a generic inverse folding model—without the need to train specialized artificial... Read more
AI-powered strategy streamlines protein engineering by integrating structural and evolutionary constraintsA team of researchers has developed a method that could transform the field of protein engineering. The new approach, called AI-informed Constraints for protein Engineering (AiCE), enables rapid and efficient protein evolution by integrating structural and evolutionary constraints into a generic inverse folding model—without the need to train specialized artificial... Read more
© 2024 FreshHive.ca - Lifestyle News. Served Fresh.
