-
 AI-powered vision gives meaning to wildfire chaosHow wildfires spread is more variable and unpredictable than Canada's standard models assume, new research from UBC Okanagan data scientists shows.... Read more
AI-powered vision gives meaning to wildfire chaosHow wildfires spread is more variable and unpredictable than Canada's standard models assume, new research from UBC Okanagan data scientists shows.... Read more -
 A new tunable cell-sorting device with potential biomedical applicationsPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) hydrogel undergoes significant but precise changes in size between 20°C and 40°C, making it an excellent candidate for use in variable-size deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) array devices. Researchers from Science Tokyo have built a tunable DLD cell-sorting platform and verified its ability to sort cancer cells of defined... Read more
A new tunable cell-sorting device with potential biomedical applicationsPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) hydrogel undergoes significant but precise changes in size between 20°C and 40°C, making it an excellent candidate for use in variable-size deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) array devices. Researchers from Science Tokyo have built a tunable DLD cell-sorting platform and verified its ability to sort cancer cells of defined... Read more -
 Researchers develop sustainable technology to extract isoflavones from soybean mealA study conducted at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, has proven the efficiency of a sustainable process for extracting isoflavones from soybean meal that increases their bioavailability.... Read more
Researchers develop sustainable technology to extract isoflavones from soybean mealA study conducted at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, has proven the efficiency of a sustainable process for extracting isoflavones from soybean meal that increases their bioavailability.... Read more -
 Technology boosts hop production in Brazil and paves way for new bioproductsDespite being the third-largest producer and consumer of beer worldwide, Brazil depends almost entirely on hop imports. Less than 1% of the ingredient responsible for the bitterness, aroma, and flavor of beer is grown locally. However, a new project involving Brazilian scientists and producers in the Vale do Ribeira region... Read more
Technology boosts hop production in Brazil and paves way for new bioproductsDespite being the third-largest producer and consumer of beer worldwide, Brazil depends almost entirely on hop imports. Less than 1% of the ingredient responsible for the bitterness, aroma, and flavor of beer is grown locally. However, a new project involving Brazilian scientists and producers in the Vale do Ribeira region... Read more -
 Neural network helps detect gunshots from illegal rainforest poachingWildlife poaching remains a major conservation concern. Technological advancements have enabled webs of acoustic sensors to be deployed throughout rainforests, creating the possibility of real-time alerts to the sounds of gun-based poaching.... Read more
Neural network helps detect gunshots from illegal rainforest poachingWildlife poaching remains a major conservation concern. Technological advancements have enabled webs of acoustic sensors to be deployed throughout rainforests, creating the possibility of real-time alerts to the sounds of gun-based poaching.... Read more -
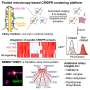 CRISPR-based platform shines a brighter light on the link between cells and diseaseFor years, Yale researchers David Breslow and Mustafa Khokha have worked together with a similar challenge in their sights—trying to capture the interplay between certain genes and the pediatric developmental disorders they cause.... Read more
CRISPR-based platform shines a brighter light on the link between cells and diseaseFor years, Yale researchers David Breslow and Mustafa Khokha have worked together with a similar challenge in their sights—trying to capture the interplay between certain genes and the pediatric developmental disorders they cause.... Read more -
 Smart hydrogels act as 'micromachines' to squeeze and study living cellsWithin tissues, cells are embedded in complex, three-dimensional structures known as the extracellular matrix. Their biomechanical interactions play a crucial role in numerous biological processes. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light (MPL) have now developed a novel lab-on-a-chip system based on intelligent hydrogel structures, which... Read more
Smart hydrogels act as 'micromachines' to squeeze and study living cellsWithin tissues, cells are embedded in complex, three-dimensional structures known as the extracellular matrix. Their biomechanical interactions play a crucial role in numerous biological processes. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light (MPL) have now developed a novel lab-on-a-chip system based on intelligent hydrogel structures, which... Read more -
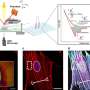 Zapping stem cells could boost growth of new tissues and organsScientists in Melbourne have discovered how tiny electrical pulses can steer stem cells as they grow, opening the door to new improved ways of creating new tissues, organs, nerves and bones.... Read more
Zapping stem cells could boost growth of new tissues and organsScientists in Melbourne have discovered how tiny electrical pulses can steer stem cells as they grow, opening the door to new improved ways of creating new tissues, organs, nerves and bones.... Read more -
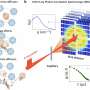 X-ray laser offers new look at protein movement inside cellsAt European XFEL, researchers have observed in detail how the vital iron protein ferritin makes its way in highly dense environments—with implications for medicine and nanotechnology.... Read more
X-ray laser offers new look at protein movement inside cellsAt European XFEL, researchers have observed in detail how the vital iron protein ferritin makes its way in highly dense environments—with implications for medicine and nanotechnology.... Read more -
 Adjustable DNA 'shield' can control timing and rate at which mRNA produces proteins in vivomRNA, widely known from the COVID-19 vaccine, is not actually a "therapeutic agent," but a technology that delivers the blueprint for functional proteins in the body and induces therapeutic effects. Recently, its application has expanded to cancer and genetic disease treatments, but mRNA therapeutics have caused serious side effects such... Read more
Adjustable DNA 'shield' can control timing and rate at which mRNA produces proteins in vivomRNA, widely known from the COVID-19 vaccine, is not actually a "therapeutic agent," but a technology that delivers the blueprint for functional proteins in the body and induces therapeutic effects. Recently, its application has expanded to cancer and genetic disease treatments, but mRNA therapeutics have caused serious side effects such... Read more -
 AI in bee hives: Monitoring system remotely predicts flowering periodsA monitoring system devised by the University of Cordoba ascertains the flowering stages of each hive, with high precision, exploiting data on bees' behavior.... Read more
AI in bee hives: Monitoring system remotely predicts flowering periodsA monitoring system devised by the University of Cordoba ascertains the flowering stages of each hive, with high precision, exploiting data on bees' behavior.... Read more -
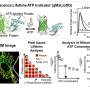 Quantitative ATP imaging can measure cellular energy in real timeResearchers at the Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, have developed a method for quantitative imaging of ATP levels inside living cells. The study, published in Nature Communications, introduces qMaLioffG, a genetically encoded fluorescence lifetime indicator that allows scientists to observe how cells produce and consume energy in real... Read more
Quantitative ATP imaging can measure cellular energy in real timeResearchers at the Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, have developed a method for quantitative imaging of ATP levels inside living cells. The study, published in Nature Communications, introduces qMaLioffG, a genetically encoded fluorescence lifetime indicator that allows scientists to observe how cells produce and consume energy in real... Read more -
 Label-free technique unlocks secrets of bacterial shape-shiftingScientists have long known that bacteria come in many shapes and sizes, but understanding what those differences mean has remained a major challenge, especially for species that can't be grown in the lab.... Read more
Label-free technique unlocks secrets of bacterial shape-shiftingScientists have long known that bacteria come in many shapes and sizes, but understanding what those differences mean has remained a major challenge, especially for species that can't be grown in the lab.... Read more -
 Artificial membranes mimic life-like dynamics through catalytic chemical reactionsUsing catalytic chemistry, researchers at Institute of Science Tokyo have achieved dynamic control of artificial membranes, enabling life-like membrane behavior. The work is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.... Read more
Artificial membranes mimic life-like dynamics through catalytic chemical reactionsUsing catalytic chemistry, researchers at Institute of Science Tokyo have achieved dynamic control of artificial membranes, enabling life-like membrane behavior. The work is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.... Read more -
 RNA in action: Filming ribozyme self-assemblyRNA is a central biological macromolecule, now widely harnessed in medicine and nanotechnology. Like proteins, RNA function often depends on its precise three-dimensional structure. A recent study published in Nature Communications by Marcia group, has captured, for the first time, a ribozyme in motion—almost frame by frame. The researchers recorded... Read more
RNA in action: Filming ribozyme self-assemblyRNA is a central biological macromolecule, now widely harnessed in medicine and nanotechnology. Like proteins, RNA function often depends on its precise three-dimensional structure. A recent study published in Nature Communications by Marcia group, has captured, for the first time, a ribozyme in motion—almost frame by frame. The researchers recorded... Read more
© 2024 FreshHive.ca - Lifestyle News. Served Fresh.
